Clash of Neurological Titans: Guillain-Barré Syndrome vs Acute Transverse Myelitis
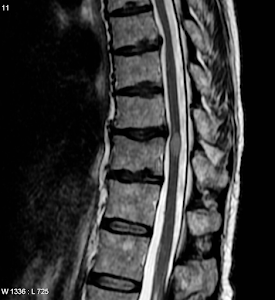
Guillain-Barré Syndrome vs Acute Transverse Myelitis Both Transverse myelitis and Guillain-Barre syndrome are immunologically caused polyneuropathies with significant clinical implications. Although no precise genetic risk loci have been identified as of yet, both are believed to have a hereditary tendency. Both are regarded as autoimmune diseases, but the exact causes are not yet known. Both may be brought about by molecular mimicry, especially from vaccinations and infectious agents, but it is obvious that host factors and co-founding host responses will affect the natural history and susceptibility to disease. The symptoms of GBS, an acute inflammatory immune-mediated polyradiculoneuropathy, include discomfort, tingling, and increasing weakness as well as autonomic dysfunction. In acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, immune destruction occurs specifically at the myelin sheath and associated Schwann-cell components; in acute motor axonal neuropathy, however, th...
